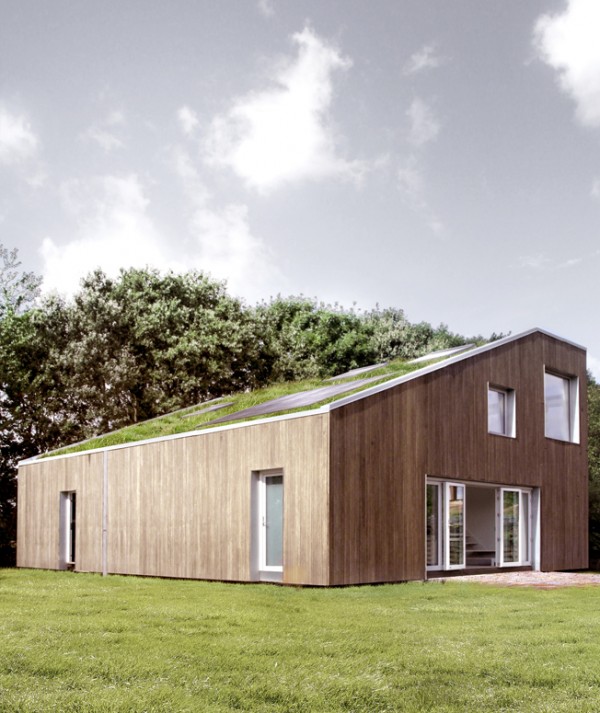
My first act of gorilla gardening was for my friend Joe. He’d worked for many years on building a home whenever he had money available and help from friends. The place was a cluttered construction site for a long time. But as the building was nearly completed, and the construction debris cleared away, there was room in a sunny spot for a small garden. I knew Joe wanted to grow some of his own food and where he intended to put a garden so when he left town for a week, I made my move.
I collected some discarded 4×4’s and some left over fencing and piled them into my station wagon along with some garden starts and headed over to Joe’s. It’s a lovely place at the end of a dirt road. I got to work with my digging fork and turned sod, weeded and formed beds. I dug holes and erected the posts and fencing. Then I planted the seeds and starts, salad greens, squash, peas and beans to climb the fence and a bed for perennials like rhubarb, herbs and raspberries. I watered it all from the rain barrel. When Joe came home and found it he was delighted. Since then his garden has expanded to 5 times the size of the original.
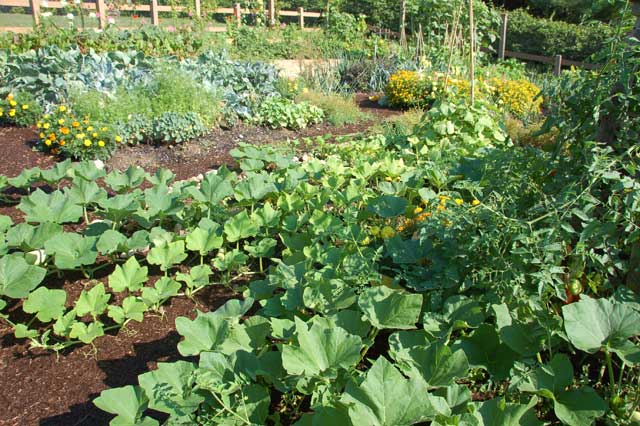

I live on a small lot in town. The previous owner traveled often so his landscaping was concrete and grass. Now after 5 years, there’s a native plant garden on the shady side of the house with vine maple and crabapple trees, salal, Oregon grape, red flowering currant, columbine and wild ginger. In the sunniest part of the yard, right up against the sidewalk, I have my espaliered fruit trees with 10 different kinds of fruit grafted on to 4 trees. There are 2 blueberry bushes and strawberry plants. In the beds there are potatoes, squash, peas, salad greens, broccoli, cauliflower and winter greens. A stately rhubarb fills out one corner and cosmos bloom by the fence. What a delight to grow my own produce. I planted greens last August to winter over so I’m eating chard, collards, kale and beets year round. The chard with their red and yellow stems brighten up the flower beds.
Gardening on a small lot
It took a while for me to figure out what grows best here in the Northwest and in my yard. Then I had to get used to eating what I grow. But now I’m totally addicted. I take some with me when I travel.
This spring my elderly neighbor said she wasn’t going to garden this year. My ears perked up. I asked, and she said to “Garden as if it was your own.” That garden has been under cultivation for decades so mostly what I’m doing is weeding and uncovering the volunteers. There’s lettuce, chard and garlic in abundance. I added a few squash and beans and covered them with a floating row cover to keep the deer and squirrels at bay.
Another friend is moving from Whidbey where he’s lived for thirty years. He has a well-established landscape. I’ve been weeding with him there getting his house ready to sell and hearing about his projects restoring an old house in Port Townsend where he’s planning to move. Last week while in Port Townsend, I put a couple of big pots on his porch, filled them with potting soil and added salad starts and a couple of squash. A friend 2 doors down said she’d keep them watered. My friend was touched to find them the next day. I love guerrilla gardening.