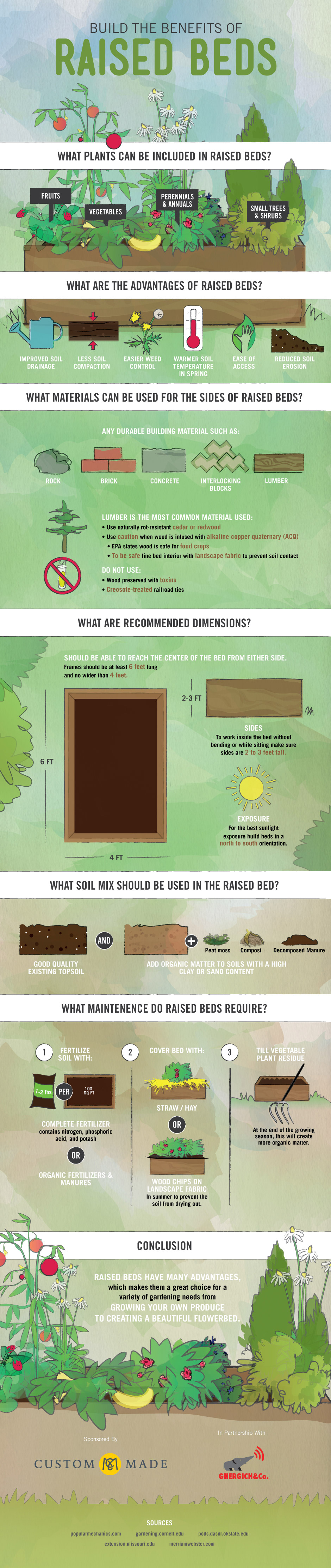
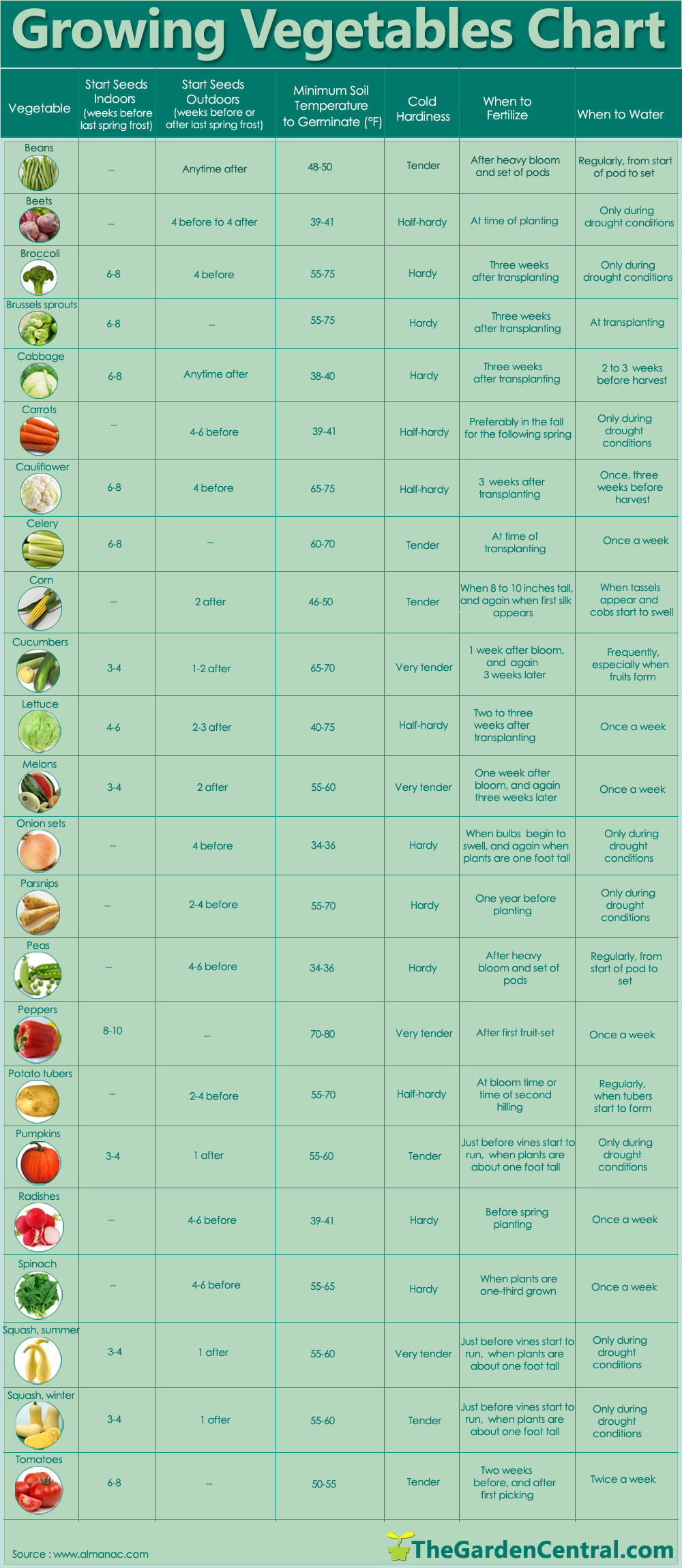
Are you looking to incorporate more herbs into your diet for holistic health? Herbs have been used for centuries as natural remedies for a variety of ailments and are packed with nutrients that can have a wide range of health benefits when consumed regularly. In this article, we’ll introduce you to the top 20 herbs that you should consider adding to your diet for optimal wellness. From turmeric to mint, these herbs have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, support immune health, and even improve memory and cognitive function. Incorporating these herbs into your meals is a simple way to add flavor and nutrients to your diet.

Herbs have been used for centuries as natural remedies for a variety of ailments. They are packed with nutrients and have a wide range of health benefits when consumed regularly.
Here are the top 20 herbs that you should consider adding to your diet for holistic health:
- Turmeric: This spice is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and is often used to treat pain and swelling.
- Ginger: This herb is commonly used to treat nausea, but it also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Garlic: This herb has been shown to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as well as reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Basil: This herb is high in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
- Rosemary: This herb has been shown to improve memory and cognitive function. It also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Oregano: This herb is high in antioxidants and has antimicrobial properties, making it a good choice for supporting immune health.

- Sage: This herb has been shown to improve memory and cognitive function in older adults. It also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Thyme: This herb is high in antioxidants and has antimicrobial properties. It is also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
- Mint: This herb is known for its refreshing taste and has been used to help with digestion and relieve nausea.
- Cilantro: This herb is high in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
- Parsley: This herb is high in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
- Chives: This herb is high in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
- Tarragon: This herb has a unique flavor and is high in antioxidants. It has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties.
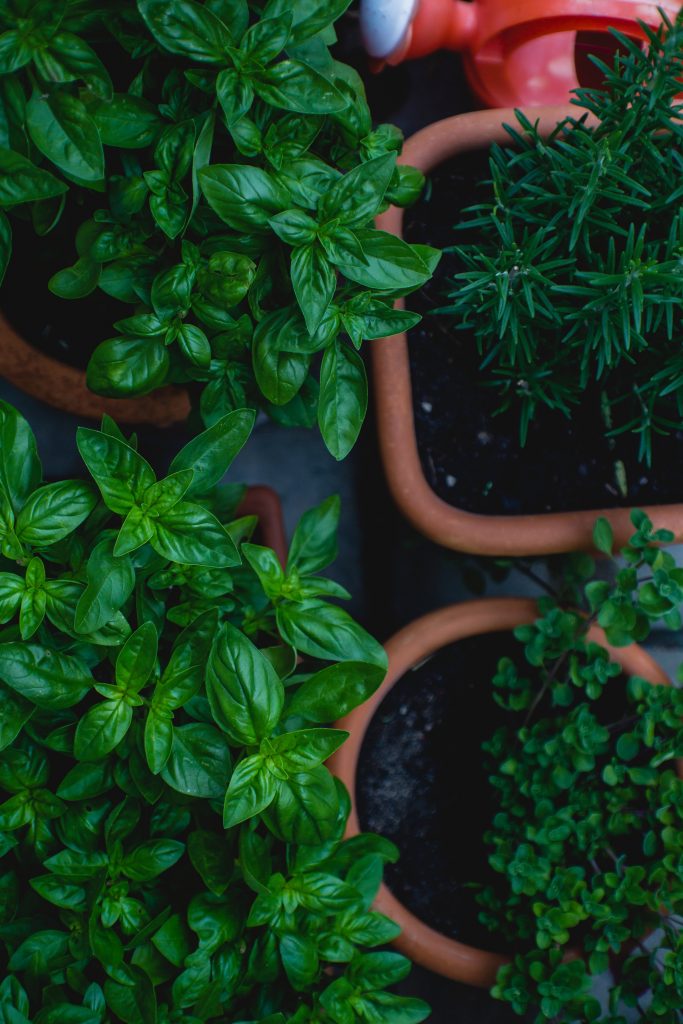

- Marjoram: This herb has a sweet, warm flavor and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Fennel: This herb has a licorice-like flavor and has been used to help with digestion and to reduce bloating.
- Dill: This herb has a refreshing, light flavor and has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Coriander: This herb has a citrusy flavor and has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Cumin: This herb has a warm, earthy flavor and has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Caraway: This herb has a warm, sweet flavor and has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Cardamom: This herb has a sweet, floral flavor and has been used to help with digestion and to freshen breath.
Incorporating herbs into your diet is a simple way to add flavor and nutrients to your meals. Be sure to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new herbs to your diet, especially if you are taking any medications or have any underlying health conditions.